water permeability test soil|typical permeability values of soil : makers FIELD MANUAL 110 Table 17-1.—A glossary of abbreviations and definitions used in permeability calculations K = Coefficient of permeability in feet (meters) per year under a unit gradient. Q = Steady flow into the well in ft3/sec [m3/sec]. H = The effective head of water in the well in feet (m). For packer tests, determining the effective head is defined Buscar resultados para: Papo Astral. Papo Astral admin 202.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Chegaram as Fichas Rápidas!! Agora você já pode fazer as suas apostas a partir de casa e apostar nos nossos quiosques de forma rápida. Visite já o .
Soil permeability (hydraulic conductivity) is the rate at which water flows through soil materials. It is an essential characteristic across a broad spectrum of engineering and earth-science disciplines. See morePERMEABILITY TEST METHOD A. SCOPE. The permeability test is a measure of the rate of the flow of water through soil. In this test, water is forced by a known constant pressure .
Soil permeability is the quality of a soil enabling it to transmit air or water through the soil pores. Texture, structure, cracking, and the amount of organic matter influence the permeability. 9.8: Soil Permeability - Geosciences LibreTexts
The coefficient of permeability varies with the void ratio as e/sup>/(1+e). For a given soil, the greater the void ratio, the higher the value of the coefficient of permeability. Here 'e' is the void ratio. Based on other concepts it has been established that the permeability of a soil varies as e 2 or e 3 /(1+e). Whatever may be the exact .FIELD MANUAL 110 Table 17-1.—A glossary of abbreviations and definitions used in permeability calculations K = Coefficient of permeability in feet (meters) per year under a unit gradient. Q = Steady flow into the well in ft3/sec [m3/sec]. H = The effective head of water in the well in feet (m). For packer tests, determining the effective head is definedInfiltration and permeability describe the manner by which water moves into and through soil. Water held in a soil is described by the term water content. Water content can be quantified on both a gravimetric (g water/g soil) and volumetric (ml water/ml soil) basis. The volumetric expression of water content is used most often.
Variable head permeability test is one of several techniques by which the permeability of soil is determined. . 75micron wire gauge, thermometer, and a source of de-aired water. Soil Specimen Preparation Disturbed Soil Sample. Take 2.5-kg soil from a thoroughly mixed air-dried or oven-dried material and evaluate its moisture content. Remove .
Apparatus for Constant Head Permeability Test. Permeameter mould, internal diameter = 100mm, effective height =127.3 mm, capacity = 1000ml. . Take a small specimen of the soil in a container for the water content determination. Remove the collar and base plate. Trim the excess soil level with the top of the mould.
The SI unit for permeability is the square metre (m 2).A practical unit for permeability is the darcy (d), or more commonly the millidarcy (md) (1 d ≈ 10 −12 m 2). The name honors the French Engineer Henry Darcy who first described the flow of water through sand filters for potable water supply. Permeability values for most materials commonly range typically from a fraction to . What is Soil Permeability? Soil permeability is a measurement dictating how quickly water can pass through a soil sample. We use permeability testing to assess how effectively soil allows water to travel through it. In general, water travels quickly through highly permeable soils and slowly through soils with low permeability.
The discharge (apparent) seepage velocity of water based on the gross cross-sectional area of the soil, or A q v However, water cannot be flowing through solid particles but only through the voids or pores between the grains. The average velocity at which the water flows through the soil pores is obtained by: A v q v s v s is called the SEEPAGE . If the depth of penetration of water is less than or equal to 25mm, the specimen passes the permeability test. If the depth of penetration of water is more than 25mm, the specimen is considered to have failed the permeability test. Record the test results in a tabular form, indicating the depth of penetration of water for each specimen and the . Alternatively, permeability may be measured in the field using insitu borehole permeability testing (e.g. [2]), and field pumping tests. . J. Hvorslev, Time lag and soil permeability in ground . Figure 2 shows a schematic representation of the test which basically works the same as the constant head permeability test, the only difference being that the water head will not be constant but diminishing over time. This test .
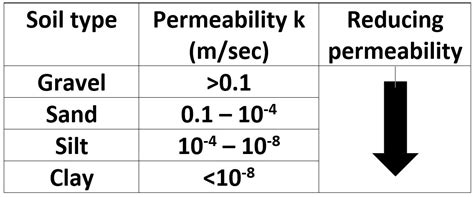
typical permeability values of soil
Permeability. Permeability is a physical property of a porous material that permits the flow or passage of water under saturated or nearly saturated conditions through interconnected voids in soil in which flow may be in the form of laminar flow or turbulent flow, practically flow problems of water in soil mechanics through its interconnecting voids ,in most of case flow is laminar, the .
typical permeability of soils
Permeability of soil- water strongly affects the engineering properties for most kind of soils and water is an important factor in most geotechnical problem. . Temperature during testing is 27°C. Flow through soil is laminar; Entire cross sectional area is available for flow; The constant head permeability test is usually preferred for sandy soils and the variable head permeability test for silty and clayey soils. A separate constant head method for granular soils has been recommended by .the water level in the test hole is allowed to fall and the equivalent permeability is computed from the data of the rate of fall of the water level. 2.6 Slug Method — The test done by instantaneous injection of a given quantity of ‘slug’ of water into a well, and determining the coefficient of permeability from the fall of water level.The permeability coefficient can be calculated when the water in the standpipe has reached a previously determined level. The calculation takes into account the size of the sample, the cross-sectional area of the standpipe, as well as the time it took to change the water level. Soil Permeability Testing Equipment: Permeability Cells (Flexible .
Procedure for the Falling Head Soil Permeability Test. The falling head soil permeability test works like the constant head test. The difference is that the water head will not be constant but will decrease/fall with time. The step-by-step procedures for the falling head permeability test are as follows:
Falling Head Permeability Test. This is also known as the Variable head permeability test. The head-causing flow in this method is not as constant as in the previous method. The falling head permeability test is employed for the permeability of soil like fine-grained soil, and clay. Fig.2. Falling Head PermeameterPermeability Test: This test assesses the soil’s ability to transmit water. The most common methods are the constant head permeability test and the falling head permeability test. Shear Strength Tests: These tests evaluate a soil’s ability to resist shear forces. Common shear strength tests include the Direct Shear Test, Triaxial Shear Test .
The rate of flow of water, under laminar flow conditions, through a unit cross sectional area of soil mass, under unit hydraulic gradient, is defined as coefficient of permeability. Permeability of the soil governs the magnitude of excess pore water pressure built-up in the embankment or cuttings, during consolidation process or when the .
The findings indicate that the triaxial test demonstrates the highest permeability, whereas the falling head test exhibits the lowest. . Determination of permeability of a soil-Constant head method using a flexible wall permeameter. Google Scholar. . Application of an Unknown Substance to Imitate Water Damage. Next. Open in viewer. Go to . Standard Test Methods for Water Permeability of Geotextiles by Permittivity D4491_D4491M-22 ASTM|D4491_D4491M-22|en-US Standard Test Methods for Water Permeability of Geotextiles by Permittivity Standard D4491/D4491M Standard Test Methods for Water Permeability of Geotextiles by Permittivity> new BOS Vol. 04.13 Committee D35 $ . This video shows how to perform a falling head permeability test for fine-grained soil. This test is typically performed on fine-grained soil with low permea.
The soil water characteristic curve can be used to indirectly determine the soil shear strength, permeability, change in water volume, water holding capacity and water availability.This video explains the procedure of constant head test to determine the soil permeability. This test is performed on coarse-grained soil with a high coeffic.
china gas spring life test
PERMEABILITY TEST 1. Objective The rate of flow of water, under laminar flow conditions, through a unit cross sectional are of soil mass, under unit hydraulic gradient, is defined as coefficient of permeability. Permeability of the soil governs the magnitude of excess pore water pressure built-up
free radon gas test kit colorafo springs
soil permeability test procedure
24 de mai. de 2023 · Google Authenticator adds an extra layer of security to your online accounts by adding a second step of verification when you sign in. This means that in .
water permeability test soil|typical permeability values of soil